Medical Library
Pick a Body Area
 Osteoarthritis
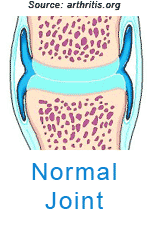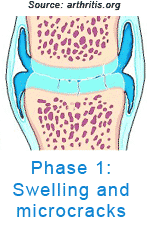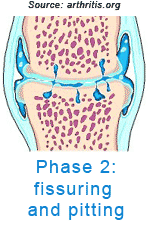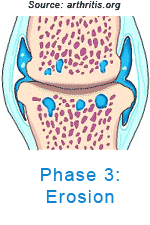
OsteoarthritisArthritis means inflammation of a joint. Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis. It is generally described as the degeneration of the cartilage pads that line the joint surfaces. Joint cartilage, called articular cartilage, covers the ends of bones and acts as a friction-free surface and a cushion. The cartilage does not have any nerve ends nor does it have a blood supply so when it is traumatized, you don't feel much pain nor does it bleed. However, over time these cartilage pads crack and wear away exposing the bone underneath (subchondral bone). The bone thickens, bone spurs (technically called osteophytes) form, and inflammation of the joint occurs.
According to the Arthritis Foundation, 21 million Americans have osteoarthritis. It affects middle-aged people as well as seniors. Factors that increase your likelihood of experiencing an osteoarthritic joint are:
- Weight - the heavier you are the more likely you will experience OA.
- Trauma - joints that have experienced trauma are more likely to develop OA.
- Infection - if your joint was infected in the past, it is more likely to develop OA.
Symptoms include joint stiffness, pain, stiffness after prolonged sitting/lying, catching and grinding of the afflicted joint, redness, warmth, swelling, and difficulty using the involved joint.
It is important that you obtain the appropriate diagnosis from your medical doctor. Once diagnosed with OA, there are some things that you can do to slow its progression. Weight loss, strengthening, physical therapy joint mobilization, aquatic exercise, ice when inflamed, heat with stiffness, and bracing the joint can all help. Ask your rehabilitation specialist which is best for you.
A common question that patients ask is, "Does glucosamine help my arthritis?" More recent studies seem to indicate that glucosamine sulfate does have a positive effect on osteoarthritis. Glucosamine is one of the "ground substances" or important molecules that make up cartilage. Adding this over-the-counter supplement to your diet may have positive effects on mild to moderate osteoarthritis. Some research indicates that glucosamine can provide pain relief and may decrease the progression of the disease. Though not conclusively proven, it is also theorized that glucosamine may even reverse the progression of the disease.
The last resort is joint replacement.
Possible Treatments
- Active Assistive Range of Motion Video
- Aerobic/Endurance Exercise Video
- Core Strengthening Video
- Cryotherapy or Cold Therapy Video
- Electrotherapeutic Modalities
- Gait or Walking Training Video
- Heat Pack Video
- Isometric Exercise Video
- Knee Joint Mobilization Video
- Knee Passive Range of Motion Video
- Knee Resistive Range of Motion Video
- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Video
- Posture Training Video
- Proprioception Exercises Video
- Physical Agents
- Soft Tissue Mobilization Video
- Stretching/Flexibility Exercise Video
- Active Assistive Range of Motion
Possible Treatment Goals
- Improve Balance
- Improve ability to bear weight/stand on the leg(s)
- Improve Fitness
- Improve Function
- Optimize Joint Alignment
- Improve Muscle Strength and Power
- Increase Oxygen to Tissues
- Improve Proprioception
- Improve Range of Motion
- Improve Relaxation
- Self-care of Symptoms
- Improve Safety
- Improve Tolerance for Prolonged Activities
Additional Resources
Disclaimer
The information in this medical library is intended for informational and educational purposes only and in no way should be taken to be the provision or practice of physical therapy, medical, or professional healthcare advice or services. The information should not be considered complete or exhaustive and should not be used for diagnostic or treatment purposes without first consulting with your physical therapist, occupational therapist, physician or other healthcare provider. The owners of this website accept no responsibility for the misuse of information contained within this website.
